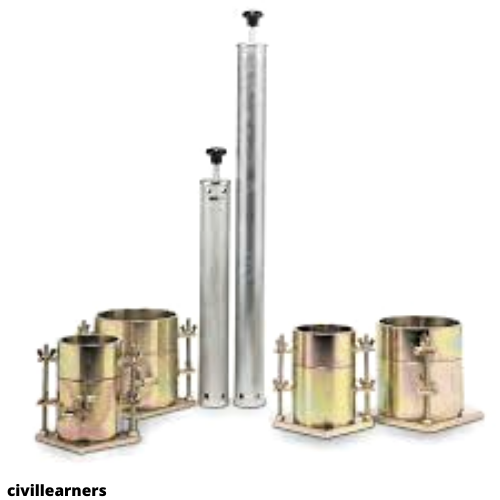
MODIFIED PROCTOR TEST
1. Objective
To determine the optimum humidity factor (OMC) and maximum dry density (MDD) values, obtain a graphical relationship to the “dry density” and “moisture content” in the form of a “compression curve”.
2. Apparatus Required
Figure 1: Proctor Mould and Metal Rammer

Metal molding (100mm diameter mold volume = 1000 cm3 and 150mm diameter volume = 2250 cm3 (according to IS: 10074-1982) & metal: Rummer according to IS: 9189-1979. (Weight = 4.9 kg)
Figure 2:Balance
Balance: capacity 10g and the minimum count is 1g and another 200g capacity and sensitivity 0.01 g
Figure 3: Sieve
4.75mm, 19mm, and 37.5mm I.S. Sieves in accordance with IS 460 (Part 1) – 1985
Figure 4: Oven
Thermostatic is regulated to maintain temperatures between 105 and 110 degrees C
Figure 5: Steel Straight Edge
To trim excessive dirt over the mold
Figure 6: Aerated Container
Taking a sample to determine the moisture content
3. Procedure
1. Take a typical portion of air-dried soil to provide about 5 kg of material passing through a 19mm IS sieve (for soils that do not crush during compaction) or about 15 kg of material passing through a 19mm IS sieve (filter this in a 19mm IS sieve during compression for crushing soils and total sample ratio) Discard the rough side after recording.
2. Add the appropriate amount of water to the soil and mix it thoroughly. Add 3% to sand and gravel soil 5% water.
The amount of water to be added to the cohesive soil should be less than 12% to 16% of the limit of plastic.
3. Weigh the base plate attached mold to the nearest 1g and record the weight as W1.
Attach expansion collar with mold. Compress the moist soil into the mold in approximately five layers equal mass, 25 shots per layer, with the help of a 4.9 kg Rammer, dropped from a height 450mm on the soil. Shots should be uniformly distributed on the surface of each layer.
The operators must ensure that the Rammer’s tube is kept free of soil so that the Rammer always falls freely.
4. After completing the compression operation, remove the extension collar and carefully level the top mold by a straight edge. Weigh the nearest 1 g with molded soil and record this weight as W2.
5. Remove the compacted soil from the mold and place it in the mixing tray. Determine the water sample Representative Sample Subject. Record the moisture content as ‘M’.
6. The rest of the soil should be broken down and the above (iii) to (v) steps should be repeated increase in soil water.
The increase for sand and gravel soils is usually 1% to 2% and increases for composite soils are usually 2% to 4%.
The total number of resolutions made must be at least five and the humidity factor should be the best moisture content, what maximum dry density occurs, is within that range.
7. To compress soil with coarse material up to 37.5 mm size, 2250 cm 3 moulds have been used. The sample, which weighs about 30 kg and passes a 37.5 mm IS sieve, is used for testing. The soil is summarized in five layers, each layer is given 55 shots of 4.9 kg rammer
4. Calculation
1. The bulk density, γm in g / cm3 of each compressed sample is calculated from the following equation.
γm = (W2 – W1) / Vm
Where,
W1 = Weight in g of mould + base plate
W2 = Weight in g of mould + base plate + soil
Vm = Volume of mould i.e. 1000 cm3.
2. Dry density, γd in g / cm3 of each compact sample is calculated from the following equation.
γd = 100 γm / (100 + M)
Where,
γm = Bulk density of soil in g/cm3. M = Moisture content of the soil
You may also like: Soil structure
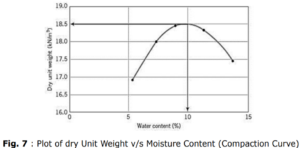
5. Graph
The dry concentrations obtained in a series of decisions, γd, are plotted against the corresponding humidity ‘M’. Then a smooth curve is drawn through the resulting points and position maximum is determined on this curve, known as the maximum dry density (M.D.D). and the corresponding humidity is called Optimum Moisture Content (O.M.C.).
You may also like: Standard proctor test
6. Video
7. Reference
IS-2720 (Part-8): 1983 (Revised-May 2015) “Soil Test Methods: Water Factor Determination – Dry Density Relation Using Heavy Compaction”.
You may also like: Proctor compact test