SEASONING OF TIMBER
When a tree is newly felled, it contains about 50 percent or more of its own dry weight as water. This water is in the form of sap and moisture. The water is to be removed before the timber can be used for any engineering purpose. The timber is to be dried. This process of drying timber is known as the seasoning of timber.
Objects:
The seasoning of timber is carried out to achieve the following objects:
1. To allow timber to burn readily if used as fuel.
2. To decrease the weight of timber and thereby lower the cost of transport and handling.
3. To impart hardness, stiffness, strength, and better electrical resistance to timber
4. To increase the resisting power of timber, as most of the causes of the decay of timber are more or less related to moisture.
5. To maintain the shape and size of the components of the timber articles which are expected to remain unchanged in form.
6. To make timber easily workable and to facilitate operations during conversion.
7. To make timber fit for receiving treatment of paints, preservatives, varnishes, etc.
8. To make timber sales from the attack of fungi and insects.
9. To make timber suitable for gluing i.e., effectively joining two members of timber with the aid of glue.
10. To reduce the tendency of timber to crack, shrink and warp.
Methods of seasoning:
The methods of seasoning can broadly be divide into the following two categories:
1) Natural seasoning
1) Artificial seasoning
1) Natural seasoning:
In this method, the seasoning of timber is carried out by natural air, and hence it is also sometimes referred to as air seasoning.
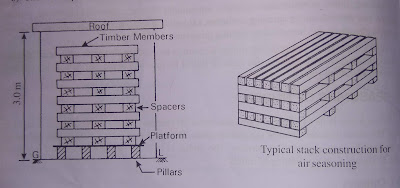
a) The timber in log form is cut and sewn into suitable sections of planks or rectangular sections of convenient size.
b) The timber pieces can either be stacked horizontally or Vertically
c) The sawn timber is stacked under a covered shed with open sides. The platform of the stack is made slightly higher about 300mm than the ground level.
d) The timber pieces are sorted out according to lengths and thickness. They are then arranged in layers, one above the other.
e) Each layer is separated by spacers of sound dry wood.
f)The length of the stack is equal to the length of timber pieces. The width and height of the stack are restricted to about 1.50 m and 3 m respectively. A distance of about 25 mm is kept between adjacent layers.
g) Similar stacks may be constructed. The minimum distance between adjacent stacks should be at least 600 mm.
Advantages:
Following are the advantages of the natural seasoning:
- Depending upon the climatic conditions, the moisture content of wood can be brought down to about 10 to 20 percent.
- It does not require skilled supervision
- It is uneconomical to provide artificial seasoning to timber sections thicker than 100 mm, as such sections dry very slowly
- This method of seasoning timber is cheap and simple.
Disadvantages:
Following are the disadvantages of the natural seasoning:
- As the process depends on the natural air, it sometimes becomes difficult to control it.
- The drying of different surfaces may not be even and uniform.
- If ends of thick sections of timber are not protected by suitable moisture-proof coating, there
- are chances for end splitting,
- If not properly attended the fungi and insects may attack timber during the process of seasoning.
- The moisture content of wood may not be brought down to the desired level.
- The process of seasoning is very slow and it usually takes about 2 to 4 years to make timber fit for the work of carpenter.
2) Artificial seasoning:
Methods of artificial seasoning:
The various method of artificial seasoning is as follows:
- Boiling
- Chemical seasoning
- Electrical seasoning
- Kiln seasoning
- Water seasoning
- Solar drying or Solar kiln seasoning
- Microwave seasoning
- Boiling:
In this process the timber is immersed in water and water is then boiled or exposed to steam spray. The timber gets seasoned quickly by this process. It is an expensive process. This method is suitable for use on small scale.
- Chemical seasoning:
This is also known as salt seasoning. In this method, the timber is immersed in a solution of suitable salt. It is then taken out and seasoned in an ordinary way. The interior surface of timber dries advance of exterior one and chances of formation of external cracks are reduced.
- Electrical seasoning:
In his method, the use is made of high-frequency alternating currents. The timber when it is green offers less resistance to the flow of electric current.
The resistance increases as the wood dry internally which also results in the production of heat. This is the most rapid method of seasoning. This method is used for a special type of timbers such as the manufacture of plywood.
- Kiln seasoning:
This method is commonly used for seasoning timber on a large scale. Timber can be seasoned to any moisture content by this process.
In this method, the drying of timber is carried out inside an airtight chamber or oven. The sawn timber is stacked in a kiln chamber.
- Water seasoning:
In this process, the log of wood is kept completely immersed in a running stream of water. The longer end of the log is kept pointing upstream.
The timber is taken out after a period of 2 to 4 weeks. During this period, the sap contained in timber is washed away by water. Then the log is. taken out of the water and allowed to dry under a shed having a free circulation of air.
Water seasoning is a quick method but it reduces the elasticity and durability of the timber and makes it brittle.
Advantages:
As immersion in water causes more rapid and regular drying, the tendency of wood to shrink
or warp is reduced
As all the organic food materials present in the sapwood are washed off, the wood is rendered
less liable to be eaten away by worm or decay by dry rot.
Disadvantages:
The process reduces the elasticity and durability of the timber.
The timber is rendered brittle.
- Solar drying or Solar Kiln Seasoning:
Solar seasoning offers a compromise between the low energy requirement of air drying and the speed of kiln drying. Kiln drying reduces the time by 50 to 75%. but at higher costs. An economic
alternative is to use solar-heated kilns. Because the energy input is variable. the kilns often have effective insulation to hold the heat inside at night time. Solar heat is collected by a series of black pained solar panels: collectors transport heated fresh air into the seasoning chamber, heated air is
circulated by two large fans, the humid air is released through a series of vents. Solar drying, which
can take nearly twice the time required for kiln-drying, is well suited to high-grade applications such
as furniture.
- Microwave Seasoning:
Microwave seasoning is an established technology in Canada and North America. It consists of directing pulsed microwave energy into layers of timber in a manner that will drive the moisture
out of the timber at rates that will not cause seasoning degrade. The process has the ability to
deliver energy that can be varied from second to second to suit the moisture content of the timber
at the time.
Advantages of artificial seasoning:
1. The defects such as shrinkage, cracking, and warping are minimized.
2. The drying is controlled and there are practically no chances for the attack of fungi and
insects.
3. The drying of different surfaces is even and uniform.
4. It considerably reduces the period of seasoning.
5. There is better control of the circulation of air, humidity, and temperature.
6. The wood becomes more suitable for painting, gluing, etc.
7. The wood with desired moisture content may be obtained by artificial seasoning.
Comparison of Air Seasoning and Kiln Seasoning:
Air Seasoning:
- It is a slow process.
- It is simple and economical.
- It is difficult to reduce moisture content below 15 to 18%.
- Air seasoned timber is more amenable to attacks of insects and fungi.
- It requires more stacking space.
- It gives stronger timber.
- It is a quick process
- It is quite technical and expensive.
- Moisture content can be reduced to any desired level
- Kiln seasoned timber is less amenable to attacks of insects and fungi.
- It requires less stacking space
- A little weaker timber is obtained.